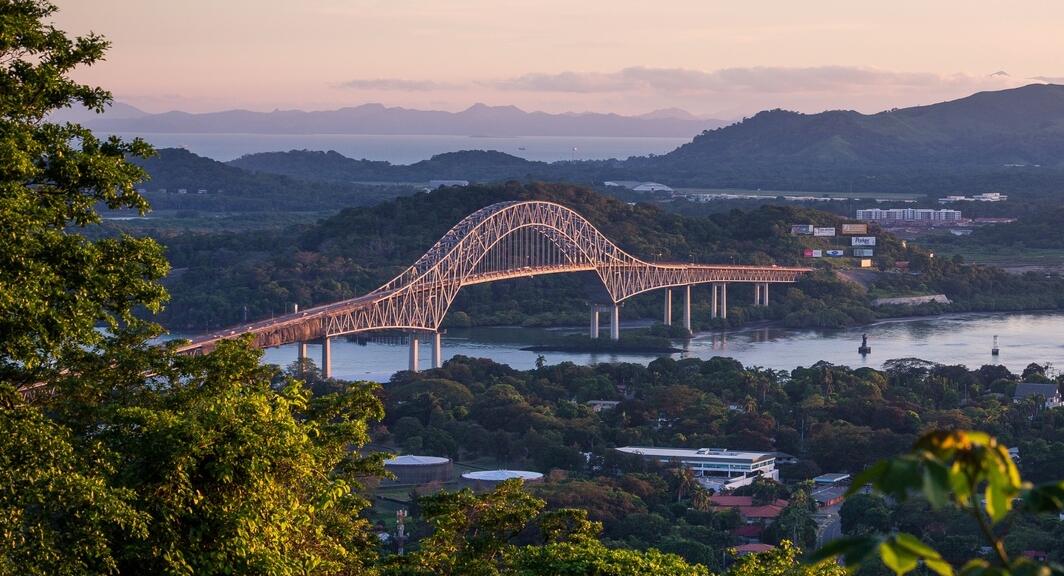
Panama is a republic furthest southeast of Central America. The elongated, S-shaped country forms a link between North America and South America. Panama borders Costa Rica in the west and Colombia in the east and lies between the Caribbean Sea in the north and the Pacific Ocean in the south. The Panama Canal intersects the country and is the transit point for much of world trade. The capital is Ciudad de Panamá ( Panama City ).
National anthem is ‘Himno Istmeño’.
Panama (the name) is of indigenous origin and means ‘abundance of fish’ or ‘abundance of butterflies’.
Geography and environment
The central part of Panama, which is owned between North and South America, is a lowland with tertiary rocks and swamps. The rest of the country has mountain chains east-west. In the east the mountain ranges are low while the interior consists of plains. To the west, there are many mountains, with the Vólcan de Chiriqui, 3,475 meters above sea level, as the country’s highest peak. In the Darien area towards Colombia there is dense rain forest. The country has almost 500 watercourses. Central parts of the Río Chagres, which is one of the few wide rivers, is formed by Lake Gatún, an artificial lake that forms part of the Panama Canal.
The climate is tropical. Daytime temperatures are approx. 30-32 o C. The Pacific Ocean temperatures are somewhat lower than the Caribbean. Almost all rainfall falls in the rainy season from May to December. It rains 1,300-3,000 millimeters a year, and more in the Caribbean than in the Pacific. The dry season is in January-May.
The lowlands have savannah in drier areas, otherwise it is tropical rainforest. In the mountains it is cooler with montane rainforest. There are more than 2,000 species of flower plants.
The rainforest has a very rich wildlife, with 218 species of mammals, including monkeys, jaguars, cougars, ozelot, golden hare, tapir, guinea pigs, sloths, harvesters and giant ants. About 850 species of birds nest, such as parrots, toucans and hummingbirds. There are many reptiles and amphibians. Examples of snakes are buoys and the poisonous lance snake. In the sea there are many species of crustaceans and fish such as tuna,tarpon, barracudas and sharks.
People and society
The population is very composed. Fertilizers (mixed indigenous people and Europeans) make up 70 per cent, indigenous people and African origin 14 per cent, white ten per cent and indigenous people, distributed among several peoples (including cúna, guayamí, chocó), six per cent.
Most of the settlement is on the Pacific side. More than half of Panama’s population lives in the Panama City – Colón corridor. 76 percent of the population lives in urban areas (2013).
Life expectancy at birth is 81.2 years for women and 75.5 years for men. 27.4 percent of the population is under 15 (2014).
Spanish is the official language. English is also widely used; many Panamans are bilingual. Indigenous languages are spoken in parts of the country.
85 percent of the population are Roman Catholics. Protestants make up 15 percent.
State and politics
Panama is a republic and a parliamentary democracy. Parliament, Asamblea Nacional, has 71 representatives elected for 5 years. The president is both head of state and head of government and is elected for 5 years.
Panama is divided into 10 provinces and 3 autonomous indigenous reserves.
Regular defense forces were abolished in 1990. Panama’s public security forces include the National Police (PNP), the National Air and Naval Service (SENAN) and the National Border Service (SENAFRONT). See abbreviationfinder.org.
Panama is a member of, for example, the United Nations and the United Nations Special Organizations, the World Health Organization, the World Trade Organization and the Organization of American States.
History
People immigrated to the North and South America owned estates, and a small number of people lived there when the Spanish Rodrigo de Bastidas came from Venezuela in 1501 to look for gold. The following year Kristoffer Columbus came and established a short-lived colony in Darien. The Vasco Núñez de Balboa crossing owned the Pacific Ocean in 1513 and the area became the crossroads and marketplace of Spain’s empire in the New World. Gold and silver came in from South America, were shipped over owned and loaded into ships sailing to Spain; the route was named El Camino Real (Kongeveien).
In the 16th century the coast was haunted by pirate attacks and Spanish authorities had little control over the territory. A Scottish colonization in Darien in 1698 failed after a few years. In 1717, the area became part of the Viceroy of New Granada (northern South America). Panama became a province of Colombia in 1821. A railroad across the Eid opened in 1855 and carried transit goods. Panama made several attempts to disengage before the country with US support proclaimed independence in 1903. In 1914, Americans completed the construction of the Panama Canal and Colombia recognized Panama.
From 1903 to 1968, Panama was a constitutional democracy ruled by oligarchs (wealthy traders who also have political power). 1969-78 had landed military rule. Land reform was implemented and a liberal banking policy made the country a financial center in the region. In 1979, the Channel Zone formally became part of Panama. In 1984 Manuel Noriega became army commander and Panama’s real leader. The opposition probably won the election in 1989, but Noriega canceled it. In December of that year, US forces invaded the country and inaugurated Guillermo Endara as president, and the following year Noriega was captured and extradited to the United States. Panama took over the Channel Zone in 1999.
From 2006 to 2012, poverty in the country was reduced by 10 per cent and unemployment declined sharply. In 2014, Juan Carlos Varela Rodríguez became president. The Panama Canal has been expanded with a parallel channel, which opened for traffic in June 2016.
Economy and business
About a fifth of the workforce is engaged in agriculture and fishing. Bananas account for one third of Panama’s export revenue. Sugar, coffee, rice, corn, pineapple, beans and lots of tropical timber are also produced. There are some cattle and pig teams. Shrimp and anchovies are exported.
The modest industry is characterized by food production and refining of petroleum for the domestic market. The United States is its main trading partner.
Fees from passage through the Panama Canal, revenue from ships sailing under the Panama flag (convenience flag) as well as banking and tourism are important sources of revenue and dominate the service sector. Colón has a free trade area for a number of foreign companies. In 2013, 25 percent of the population was considered poor. Panama’s economy has been growing in recent years.
Knowledge and culture
It is compulsory and free schooling for children aged 6-15. There are 6-year primary and 6-year high schools. Panama has two state universities and one private university. About. 6 percent of the population is illiterate.
There are 7 daily newspapers, all in Spanish. Panama gained freedom of the press in 1990. There are approx. 200 radio stations and more than 100 television channels.
An anthology of Panamanian authors edited by the poet Mateo Ribera was first published in Spain in 1642. The tragedy ‘La politica del mundo’ from 1809 by Victor de la Guardia y Ayala is the oldest preserved Panamanian poem. The period 1821-1903, when Panama was united with Colombia, was marked by the poets of romance, including Tomás Martin Feuillet (1832-62) and Amelia Denis de Icaza (1836-1911). The country’s foremost lyricist was Ricardo Miró (1883-1940) and the first modernist was Dario Herrera (1870-1914). Ricardo Miró (1883-1940) is perhaps Panama’s greatest lyricist. Other important names are the lyricist and prose writer Rogelia Sinán (pseudonym of Bernardo Dominguez Alba, 1902-94, and the lyricist and prose writer José María Sánchez (1918-1973). Younger authors are Carlos Fong (1967-), Melanie Taylor (1972-) and Annabel Miguelena (1984-).
Panamanian music was influenced by the indigenous people’s partly polyphonic music, Spanish traditions since the 1600s and African traditions. Roque Cordero (1917–2008) is one of the country’s most famous composers. ‘Cage9’ is a well-known rock band. Other modern forms of music are ‘reggae en español,’ reggaeton ‘and’ salsa ‘.
Well-known painters are Roberto Lewis (1874-1949), Manuel Chong Nieto (1927–2010), Alfredo Sinclair (1915–2014) and his daughter Olga Sinclair (1957-). Diego Bowie (1991-) is a well-known performance artist.
Baseball is national sport. Basketball and boxing are also popular sports.