Anchorage
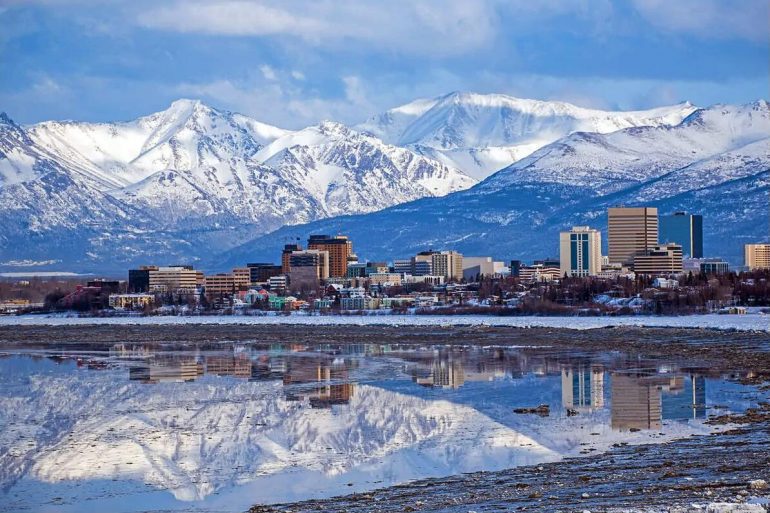
Anchorage, (anchorage ‘), a port city in southern Alaska, USA; 292,000 residents (2010), has since its founding in 1914 been an important supply city and center of transportation to other parts of Alaska. Anchorage’s strategic location led to the construction of Fort Richardson and Elmendorf Air Force Base, which together with the international airport contributed greatly to the city’s great growth after World War II. The majority of Alaska’s businesses, including oil companies, have branches in the city that also house a significant fishing industry. In addition, revenue from 3/4 million tourists who annually visit the mountain-lined and beautifully situated city. It was hit by a violent earthquake in 1964. 
Fairbanks
Fairbanks is a town on the Chena River in inner Alaska approximately 200 km south of the Arctic Circle; 32,100 residents (2010). The city emerged after gold discoveries in 1902 and was a distinct wilderness city until World War II, when the construction of military bases and the Alaska Highway ushered in a more stable period of growth. The city is the supply center for northern Alaska and the link to Anchorage in the south. via railway (1923).
Fairbanks houses the University of Alaska with 4,500 students; in summer the city is visited by a large number of tourists. Apart from the big Ice Festival in March, most activities take place from June to August; this applies, for example, to the annual World Eskimo-Indian-Olympics, which brings together Alaska’s indigenous people for competitions in all kinds of traditional skills.
Juneau
Juneau, the capital of Alaska, USA; 31,275 residents (2010). The town, which in long-distance traffic can only be reached by ship or plane, is located at the foot of Mt. Roberts (1097 m) in the Alaska Panhandle. It was elected capital in 1906 and covers an area of over 8000 km2 incl. the city of Douglas on the island of Douglas Island, with which it is connected by bridge. The economic activity was from 1880 until 1944, when the last gold mine was closed, especially linked to mining, but today the city is an administrative and educational center as well as home to a large fishery due to its ice-free port. The significant tourism business is mainly based on the summer regular service with luxury cruise ships. The excursion destinations include the Mendenhall Glacier and the temperate rainforests of the Tongass National Forest.
Ketchikan
Ketchikan, a port city on the island of Revillagigedo in southeastern Alaska, USA; 14,070 residents (2010). As a port of call on the “Alaska Marine Highway” cruise line, it is a well-visited tourist town with picturesque pole houses and a large salmon fishery. The Totem Heritage Center houses a unique collection of the original totem poles of the Tlingit Indians.
Nome
Nome, a town on the Bering Sea in Alaska, USA; 3598 residents (2010). The city arose after the gold discovery in 1898 and later became, due to the airport, an important staging post for American air supplies to the Soviet Union during World War II. After the upheavals in the Soviet Union, a collaboration has begun over the Bering Strait with e.g. scheduled flights in the summer to the sister town Providenija on the Tjuktjer Peninsula. The economy is based on tourism, fishing and reindeer husbandry in addition to goods transport (ship, plane) to Northwest Alaska. The biggest annual event is the traditional, 1688 km long dog sled race The Iditarod Sled Dog Race from Anchorage to Nome in March.
Valdez
Valdez, a port city in southern Alaska by Prince William Sound; 4020 residents (2010). Surrounded by snow-capped mountains and one of North America’s most productive glaciers, the Columbia Glacier, the city has been the shipping hub of the Trans Alaska Pipeline since 1977. In addition to the oil activities, the economy is based on fishing and tourism.
Sitka
In the southeastern part of Alaska, on the mountainous island of Baranof Island, is the city of Sitka, which was the country’s capital during the Russian rule. It was founded by Alexander Baranof as one of the first settlements ever. In 1799, Baranof built Fort St. About 9 kilometers north. Michael. However, the settlement was destroyed in 1801 by the Tlingit Indians, who originally inhabited today’s Baranof Island.
In 1804, Alexander Baranof returned from Kodiak to re-establish the government. A battle between the Russians and the Indians took place along the Indian River. The Russians gained power over this territory, while the Indians lost their independence and way of life. A Russian settlement, named “Sheetkah” in Tlingit, was built on the site of the destroyed Indian settlement, which later became Sitka. In 1822, the Indians finally left the area voluntarily. However, this family left behind numerous historic dwellings here.
The main economic resource for the town, which has over 9,000 inhabitants, is fishing and lumbering. Sitka is surrounded by countless small densely forested islands. The dominant feature of the region is the distant volcano Mt. Fuji and dozing Mt. Edgecumbe. As already mentioned, in ancient times, Sitka was the capital of Russian Alaska, but later the territory was bought from the Russian government by the Americans. Castel Hill, located in the city center, dates back to those long ago.
Sitce is the oldest national park in Alaska – the National Historical Park, which was declared a national park by the federal government in 1910. It is located on the site of the former Tlingit Indian stronghold, where the important battle between the natives and Russian invaders took place. In the museum you can find monuments from this war from 1804, a large collection of Native American totems, a canoe carved out of a tree trunk, along with their art and also examples of Native American dances and rituals. You can also see the oldest Native American products at the Sheldon Jakcson Museum, the first building in Alaska to be built of concrete.
In the center of the city stands the dominant Russian Orthodox Cathedral. Michael´s, which is the most visited and most photographed place in Sitce. The cathedral was the first building of its kind in the United States. It was built between 1844 and 1848. In 1966 it was unfortunately destroyed by fire, but later reconstructed. The city is full of Russian history. Interesting is, for example, the Russian Bishop’s House from 1842, which is the oldest undamaged Russian building in the city. It was intended for the orthodox bishop of the local community.
Thanks to its location, Sitka offers not only the historical gems of Alaska’s past, but also wild marine life. It is not a problem to see seals, otters, eagles or seagulls. More species of wild birds can be observed on the nearby island of St. Lazaria, where countless birds of the so-called Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge nest in the summer months.