The middle part of Panama, with the Channel Zone, is a low-lying swamp area with tertiary rocks. The Panama island is 55 km wide at its narrowest, and the height of the pass is only 82 meters. The other parts of Panama are characterized by mountain chains in the east-west direction. In the west, the 2000–3000 m high mountain ranges reach 3475 m. in the volcano Barú. In the east, lower chains extend along the coasts, while the interior is plain.
Climate
The area as a whole has a tropical rainy climate with an average annual temperature of 26–28 °C in the lowlands and precipitation 2000–3000 mm, mostly on the Caribbean Sea. It rains at least February – March, but without any actual drying time. There is little difference between the warmest and coldest months.
Detailed climate information about Panama on the website of the World Meteorological Organization.
Wildlife in Panama
The wildlife in Panama is very rich, especially in the rainforest. Of large mammals there are tapirs, umbilicals and deer. Monkeys, sloths, harnesses, antlers, scavengers and numerous rodents, including woodpeckers and golden hares. Jaguar and puma occur; ozlot and half bears ( raccoons, rhinos and snoals)) are common. The mammalian fauna comprises a total of 218 species, of which 14 are native (endemic). Many of the latter are highly vulnerable or directly threatened with extinction.
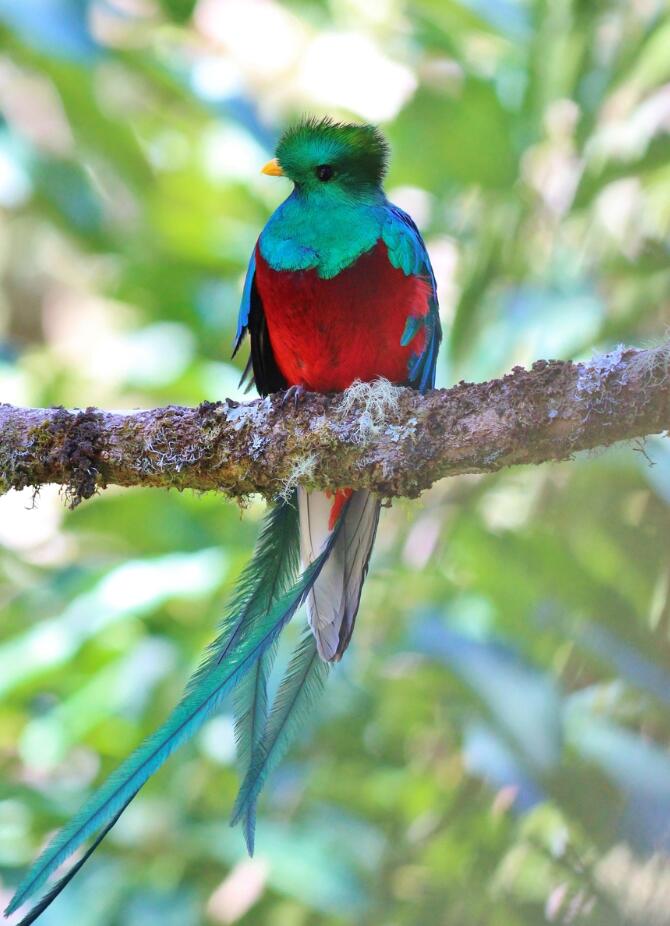
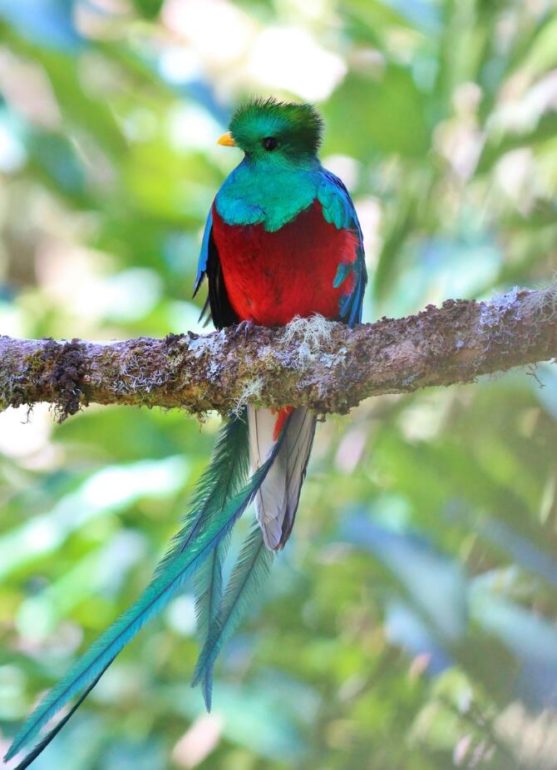
850 bird species breed in Panama, including many parrots, hummingbirds, toucans and the magnificent quetzal. An additional 100 species occur during migration or as rare guests.
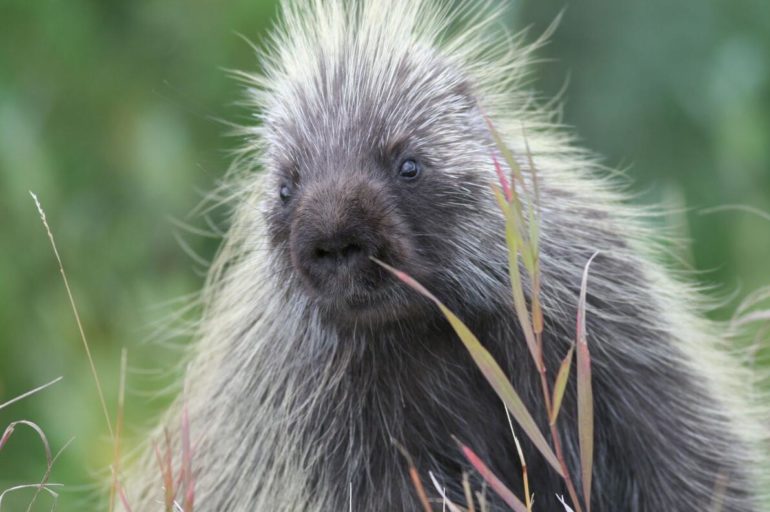
The spikes of the three-legged pigs have microscopic barbs, which means that they both penetrate easily into the skin of an attacker, easily adhere and easily work their way inward.
The reptile and amphibian fauna are many species, countless insects and other invertebrates exist. Among the snakes should be mentioned the boas (quiver snakes) and the poisonous lance snake.
The sea along the coast of Panama is rich in molluscs, crustaceans and fish. Swordfish, sailfish, marlin, tarpon, tuna, barracuda and sharks are common.
Plant life in Panama
The lowlands in drier regions have savannah vegetation, otherwise the tropical rainforest dominates. In the mountainous areas the temperature is lower and the vegetation montan rainforest. On Barro Colorado Island in the Panama Canal, perhaps the most important botanical research station is located in a tropical rainforest area.